Friends, today in this article we will learn about the types of turbines. I am going to give information about all these in a very good way. So let’s start.
Types of Turbine –
In hydroelectric power plants, when water is dropped from a height on the turbine blades, the turbine rotates, which produces mechanical energy, this mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy by generators. Water turbines have a simple design and high efficiency (about 90% at full load). They are available in different sizes up to about 10,00,000 HP and according to the size, their speed can be from 100 rpm to 1000 rpm. The following turbines are used for hydroelectric power plants –
(1) Pelton Wheel Turbine –
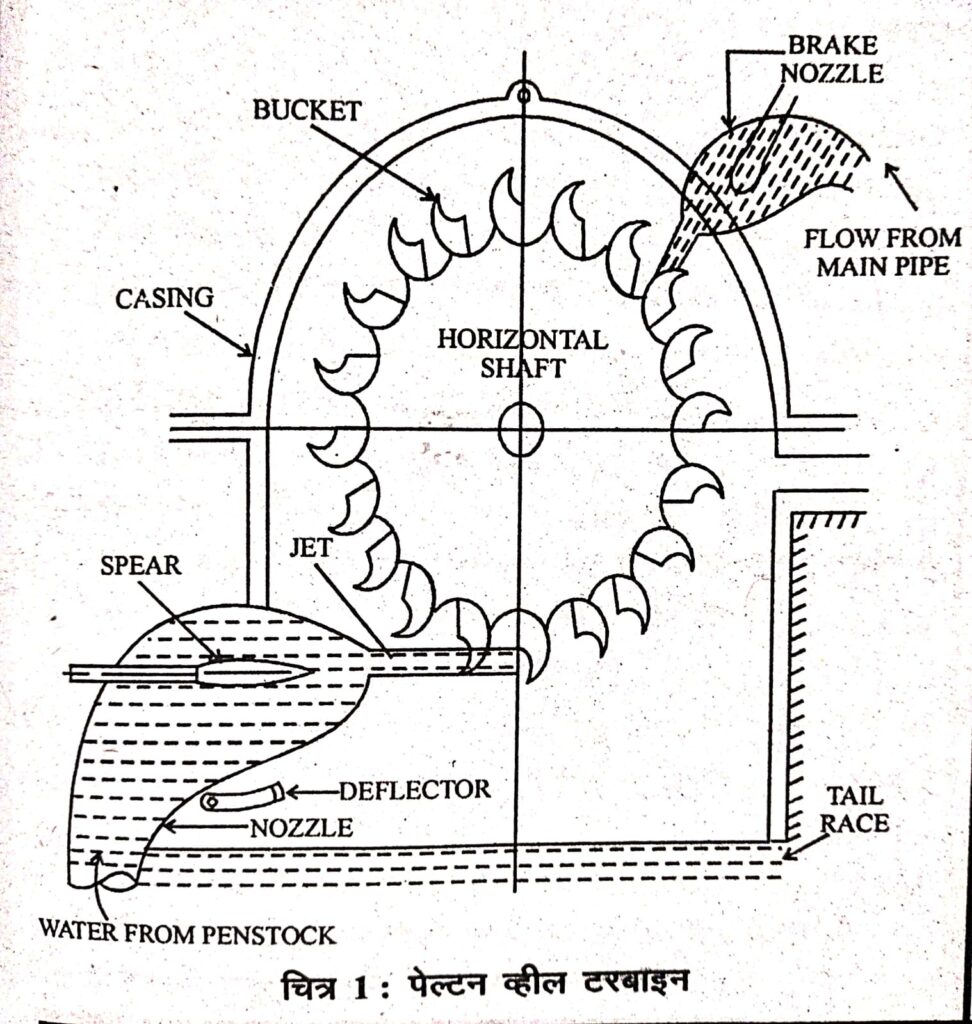
This is an impulse turbine which is used for high heads plants. The water coming out of the penstock is taken out in the form of a jet with the help of a nozzle. It has a rotor on which elliptical shaped buckets are attached.
When the water jet hits the buckets, the rotor rotates, that is, the potential energy of the water is converted into kinetic energy. After rotating the turbine, the water is discharged into the tail race. This is an impulse turbine. The amount of water coming out of the nozzle is controlled by a needle valve, which controls the speed of the turbine. The position of the needle is controlled by a governor. When the load on the turbine is less, the governor pushes the needle inside the nozzle, due to which less amount of water comes out of the mouth of the nozzle, that is, less water will hit the buckets. Similarly, when the load on the turbine increases, the governor pulls the needle out of the nozzle, due to which more amount of water comes out of the nozzle, i.e. more amount of water comes out on the buckets, as a result, more amount of water will hit the buckets.
1, 2 or 4 jets are installed in the Pelton wheel turbine as per requirement. The rotor is made of cast steel or stainless steel and the buckets are fixed on it with the help of bolts. This type of turbine is not used for low head plants because the size and diameter of its runner becomes very large, hence this turbine is not used at a head below 200 meters.
(ii) Francis Turbine –
It is suitable for medium head hydroelectric power houses. These turbines have a guide device in which stationary guide blades which are attached to the casing of the turbine together form an outer ring. Rotating blades are fitted on the runner which together form the inner ring.
Water slides over the turbine blades at a constant speed creating pressure, when the water passes over the rotating blades of the runner, its pressure and speed decrease and the turbine starts rotating. After rotating the turbine, the water is discharged through the tail race with the help of a draft tube. That is, power generation in these turbines is partly through the motion of water and partly through the difference in pressure applied on the inner buckets. This is a reaction turbine.
(iii) Kaplan Turbine –
This is a reaction turbine. Its gate and governor mechanism is similar to that of Francis turbine. But the only difference between this and Francis turbine is that in Kaplan turbine water strikes the turbine blades axially and in Francis turbine water strikes the turbine blades radially. Water comes from all sides radially inwards from the regulating gates and changes its direction in the runner to axial due to which a reaction force is generated due to which the turbine rotates.
This turbine is used in low head power houses, it works with equal efficiency on different electrical loads. It is a turbine rotating at high speed (40 rpm to 1500 rpm) due to which the cost of runner and alternator is reduced. Almost all the parts of Kaplan turbines and Francis turbines are similar.
The runner of Kaplan turbine has only 3 to 6 blades whereas Francis turbine has 16 to 24 blades. Due to less number of blades, the friction between the blades and water in Kaplan turbine is less, which increases the efficiency. In Kaplan turbine, the governor opens the valve and adjusts the angle of the blades simultaneously. Its efficiency is about 90% at different electrical loads. It is also possible to rotate the runner of this turbine in reverse, so that it can work like a pump, which makes it suitable for pumped storage plants.
(iv) Propeller Turbine –
When the turbine is rotating, the angle of its blades cannot be changed like Kaplan turbine. Its blades are cast on the hub. Its design is simple but its efficiency decreases rapidly when the electrical load decreases. Its efficiency at full load is about 92% which reduces to only 65% at half load.
What did you learn today :-
Now you must have known the types of turbines. You must have got the answer to all these questions well.
I hope you liked the information given by me, if you have any question/suggestion in your mind, then you can tell me by commenting below, I will definitely reply to your comment. If you liked this post, then you can also share it with your friends and relatives.
